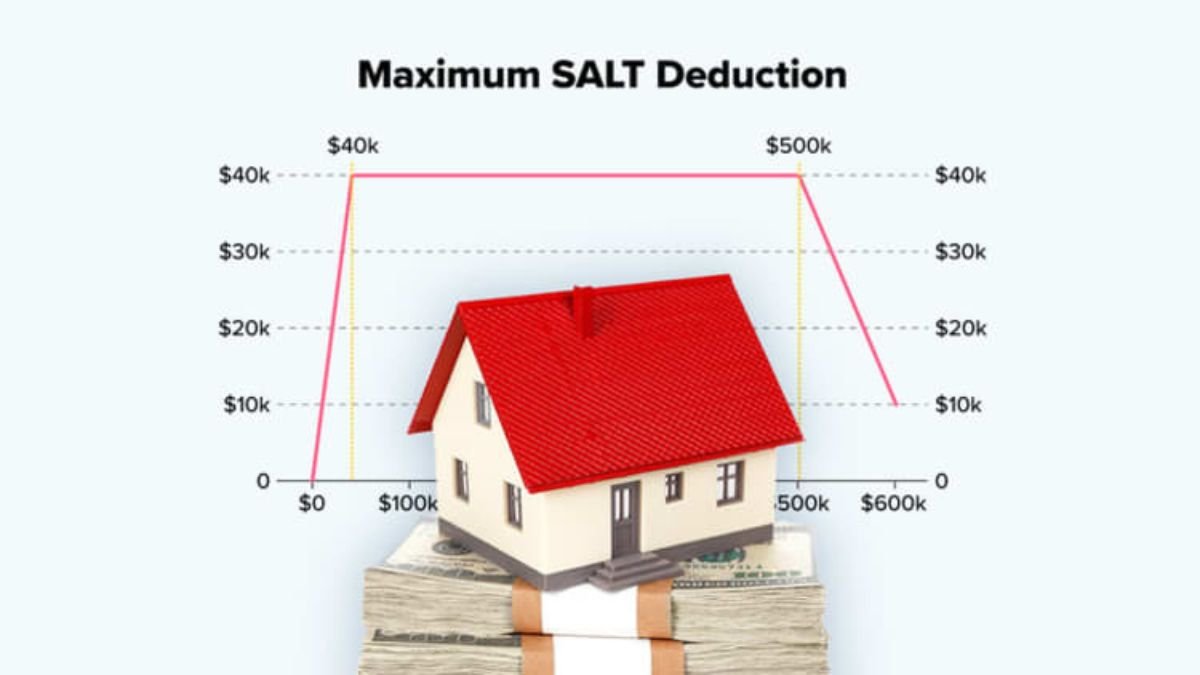
The US tax system has undergone a major change. One of the key updates from former President Donald Trump’s tax reforms is back in the news—raising the SALT deduction limit to $40,000. This change not only brings relief to taxpayers but also has a profound impact on America’s economic and political direction.
Let’s explore in detail what the SALT deduction is, who will benefit most from it, and why it has become such a major part of Trump’s tax agenda.
What is the SALT deduction?
SALT stands for State and Local Taxes. It is a tax deduction that provides US citizens with relief on their state and local taxes (such as property tax, income tax, or sales tax).
This means that if you pay taxes to your state or city, you can deduct a portion of that tax on your federal tax filing.
Previously, this limit was $10,000—meaning that an individual could claim a maximum SALT deduction of $10,000. However, under Trump’s new tax plan, this limit has been quadrupled to $40,000.
The Journey from $10,000 to $40,000—Why the Limit Was Increased
When the Trump administration implemented the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) in 2017, the SALT deduction limit was set at $10,000. The purpose was to curb the tax breaks available to high-income citizens. However, this limit severely impacted residents of many middle- and high-tax states, particularly in states like New York, California, New Jersey, and Massachusetts.
Residents in these states previously could deduct a significant portion of their substantial property and local income taxes from federal taxes. The $10,000 limit significantly increased their tax liability.
Representatives and tax policy experts from these states have long demanded an increase in this limit. Due to this pressure and political considerations, the decision has now been made to increase the SALT deduction to $40,000.
Who Will Benefit Most from This Increase?
Although this tax relief applies to all taxpayers, it will most benefit those in the higher income brackets and those living in high-tax states.
For example, families earning $250,000 or more annually and paying taxes on large properties will benefit the most from this increase.
In contrast, middle-class or lower-income taxpayers whose state or local taxes do not exceed $10,000 will not receive any significant relief from this change.
Overall, this tax change can be considered a relief package for wealthy taxpayers.
What will be the impact on the economy?
This increase in the SALT deduction could adversely affect tax revenue. According to US Treasury estimates, this could reduce federal government revenue by billions of dollars.
While supporters argue that this will encourage people to save more money, which will increase both consumption and investment, ultimately reinvigorating the economy.
Opponents, however, argue that this decision will only benefit the wealthy, while the middle class and lower classes will not receive any direct benefits.
Why is this move important from a political perspective?
The Trump administration’s tax policies have always been a center of political debate.
Increasing the SALT deduction limit is also considered a political strategy—as it provides relief to high-tax states dominated by the Democratic Party.
Trump’s move could also be seen as an attempt to ease political tensions between Republican and Democratic states. It is also a way to attract middle-class and upper-income voters ahead of the 2025 elections.
Tax Experts’ Opinion
According to tax experts, increasing the SALT deduction limit has a mixed impact.
Some experts consider this a practical reform that will provide relief to those living in high-tax states.
Others, however, call it a move made for political gain that goes against the principle of tax fairness.
According to one economist, “When you raise the SALT limit, you are actually giving higher-income families more exemptions, which could increase tax inequality.”
Its Actual Impact on the Middle Class
This change may not matter as much for the middle class as it does for the wealthy.
Because most middle-class taxpayers opt for the Standard Deduction, which already provides substantial relief.
The increase in the SALT limit will only benefit those who itemize deductions in their tax filings.
Therefore, those with limited income or low state taxes will not see any significant benefit from this new rule.
Impact on States
Many state governments are welcoming the increase in the SALT deduction limit because it could help spur investment and job creation.
States like California, New York, and New Jersey, in particular, have long demanded this reform.
However, some economists believe this relief will be temporary and will not lead to any major changes in states’ fiscal policies.
Criticism and Controversy
As soon as the announcement of raising the SALT deduction limit was made, heated debate erupted in political circles.
Some Democratic leaders called it a “tax gift to the rich.”
Conclusion
Trump’s decision to increase the SALT deduction to $40,000 is certainly a major step in the history of American tax policy.
While this change brings relief to some segments, it has also once again highlighted questions of inequality and fairness in the tax system.
FAQs
1. What is the SALT deduction in U.S. tax law?
A. The SALT (State and Local Tax) deduction allows taxpayers to deduct certain state and local taxes—such as income, property, and sales taxes—from their federal taxable income.
2. What was the previous SALT deduction limit before this update?
A. The previous SALT deduction limit was $10,000, established under the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA).
3. What is the new SALT deduction limit under Trump’s tax update?
A. Under Trump’s latest tax proposal, the SALT deduction limit has been increased to $40,000, giving taxpayers four times more room to claim deductions.